Introduction

In the realm of hardware production, the importance of a robust quality control system is paramount. But, despite stringent quality control checks, issues may occasionally arise once the product reaches the field. At such times, conducting a comprehensive Engineering Root Cause Analysis (RCA) becomes crucial. RCA is a systematic process that helps identify the primary reason for a quality control problem. For hardware products sourced from China, this process presents unique challenges. In this blog, we will explore how to carry out an RCA effectively, highlighting useful problem-solving techniques like the Five Whys Method and the Fishbone Diagram.
Understanding Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The cornerstone of an effective RCA is understanding its core objective - identifying the underlying cause of a problem, not just addressing the symptomatic issues. This approach helps to prevent the recurrence of the problem by tackling it at its root, paving the way for effective corrective measures.
Key Steps in Performing a Root Cause Analysis

Problem Identification
Begin by defining the issue precisely. Understand the nature of the problem, when and where it occurs, and its impact. Collect as much information as possible about the product defect to get a clear understanding of the problem.
Data Collection
Gather all relevant data regarding the problem. This could be from customer complaints, product return data, or feedback from field engineers. The data should include specifics about the product batch, manufacturing dates, and other details that might help trace the problem back to its origin.
Now comes the stage of brainstorming and investigating potential causes of the problem. Look beyond the obvious and delve deeper into the manufacturing process, product design, and even the supply chain. This is where problem-solving techniques like the Five Whys and the Fishbone Diagram can come in handy.
The Five Whys method involves asking "Why?" five times to peel back the layers of symptoms and reach the root cause. The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is a visual tool used to categorize potential causes of a problem into broader categories, helping to visualize the relationship between the causes and the problem.
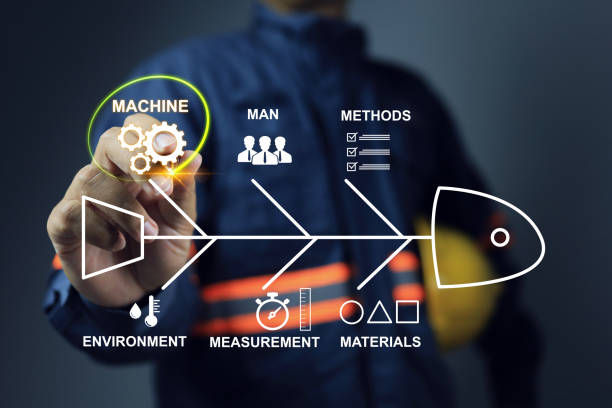
Root Cause Identification
After listing all possible causes, pinpoint the root cause—the primary reason behind the problem. You might need to conduct further tests or inspections to pinpoint this cause.
Solution Development and Implementation
Once you've identified the root cause, the next step is to develop a solution to address it. This could involve changes in the product design, modifications in the manufacturing process, or even switching suppliers. Implement the solution and monitor its effectiveness over a period of time.
Review
After implementation, review the effectiveness of the corrective measure. If the problem persists, you might need to revisit your root cause analysis and see if you missed anything. This step ensures that your RCA is leading to effective problem resolution.
Special Considerations for Hardware Products Sourced from China

When conducting an RCA for hardware products sourced from China, several unique challenges come into play:
Language and Cultural Barriers
When dealing with Chinese manufacturers, language and cultural differences can pose a significant challenge. It's essential to establish clear communication channels and use simple, unambiguous language to ensure that your RCA process is accurately understood and implemented.
Geographical Distance
The physical distance between your local team and the manufacturing site in China can make the RCA process more complicated. Using technology to bridge this gap can be very effective. For example, real-time video inspections can give your team a first-hand view of the manufacturing process.
Quality Standards
Chinese manufacturing standards might differ from those in your home country. Therefore, it's crucial to align your quality expectations with the manufacturer from the onset. Typically Quality standards are agreed upon beforehand in a Manufacturing Supplier Agreement contract; this will be a great reference point for failures and failure rates as it would be agreed before any production is started. One or two failures in batches of 2000 units should not be an issue. However, if you are getting a 3%+ failure rate then it implies an Epidemic problem is present in your production runs so production should be halted until the RCA is complete.
IP Protection
When sharing product designs or other sensitive information with the Chinese manufacturer during the RCA process, ensure that your intellectual property rights are protected; this isn't an issue if a Manufacturing Supplier Agreement is set up before production. It's an issue if IP is not agreed upon beforehand and you need to send additional equipment or diagrams to assist in the RCA process.
Carrying out an effective RCA is an ongoing, iterative process, especially for hardware products sourced from China. With diligent application, RCA can not only help you address immediate quality issues but also bring about significant improvements in your overall product quality and brand reputation. Remember, in the realm of product quality, being reactive is good, but being proactive is even better. Use the RCA as a way of shifting the team's mindset - "What was missing in your process to cause this issue?". Following this - "What other processes are lacking or might have blind spots?". You can turn the new learning into KPIs for production to keep an eye on - we wrote an article about this previously.

Conclusion
Engineering Root Cause Analysis is a critical tool in maintaining the quality and reliability of your hardware products, particularly those sourced from China. While it may seem daunting initially, following a structured, systematic approach can make the process much more manageable. Furthermore, the valuable insights gained from a thorough RCA can guide your future manufacturing strategies, ensuring that quality remains at the heart of your operations.
Navigating the waters of overseas manufacturing can be challenging, but with the right tools and strategies, it can also be a journey of continuous learning and improvement. By prioritizing Root Cause Analysis, you not only solve current problems but also lay the groundwork for sustained quality control in your future endeavours. Remember, every problem is an opportunity for growth, and every solution is a step towards excellence.

Comments